HFB200603: BTLA Antagonist
Phase I, Active, Dose Escalation Complete
Targeting the BTLA/HVEM immunosuppressive axis to activate anti-tumor immunity
BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator) is a co-inhibitory immune checkpoint structurally related to PD-1 and CTLA-4. BTLA’s expression is restricted to immune cells, including B cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and dendritic cells. Upon interaction with its ligand HVEM, BTLA induces the recruitment of SHP1 and SHP2 to suppress the proliferation and activation of B and T cells. BTLA blockade represents a promising therapeutic avenue for the treatment of cancer.
Our DIS® Approach
Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy has demonstrated efficacy across many cancers; however, many patients develop resistance to treatment, revealing a large unmet need for new immune modulators that can overcome this resistance. DIS® driven single cell immune profiling of tumors has identified high BTLA expression in exhausted CD8+ T cells in patients non- responsive to PD-1 blockade, supporting dual BTLA/PD-1 blockade as an approach to overcome anti-PD-1 resistance.
Drug Info
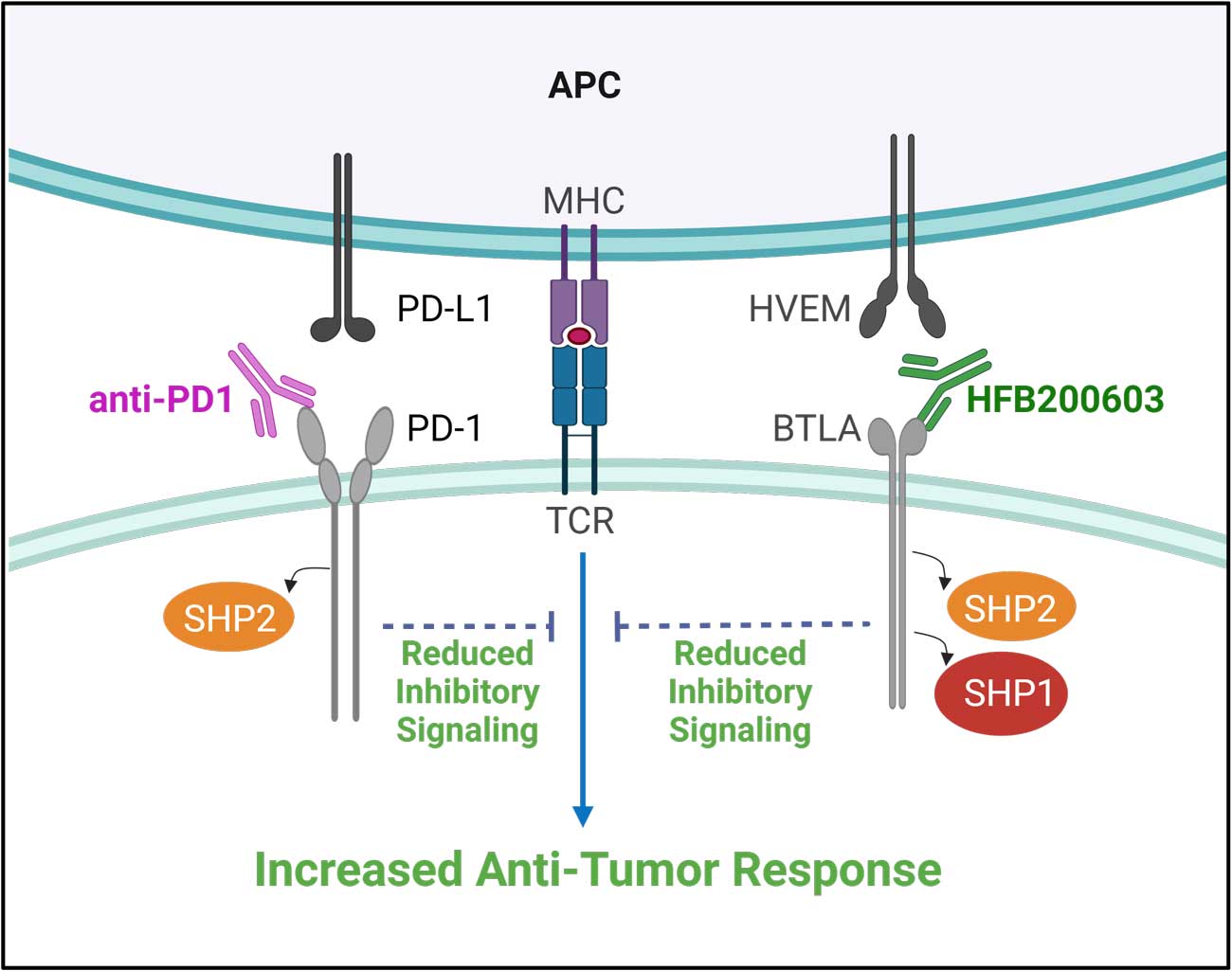
HFB200603 is a best-in-class BTLA antagonist monoclonal antibody that has been shown to reverse HVEM-mediated immune suppression. HFB200603 shows a synergistic effect with anti-PD-1 antibodies to enhance IFN-γ production and demonstrates favorable developability and pharmacokinetic profiles. HFB200603 has shown promising clinical monotherapy activity, with the desired mechanism of action on T cells and an excellent safety profile.
Clinical Trial Info
The first-in-human dose escalation and expansion study (NCT05789069) is actively enrolling patients with DIS®-selected advanced cancers for treatment with HFB200603 monotherapy or combination with anti-PD-1 tislelizumab. Identification of biomarkers predictive of response is ongoing.
